ELEC-E5500 - Speech Processing, Lecture, 4.9.2023-16.10.2023
This course space end date is set to 16.10.2023 Search Courses: ELEC-E5500
Topic outline
-
Note: Most of the videos were recorded with the previous edition of the learning material, but since the content has not changed (much), they should still match sufficiently. Let Tom know if there are significant glitches.
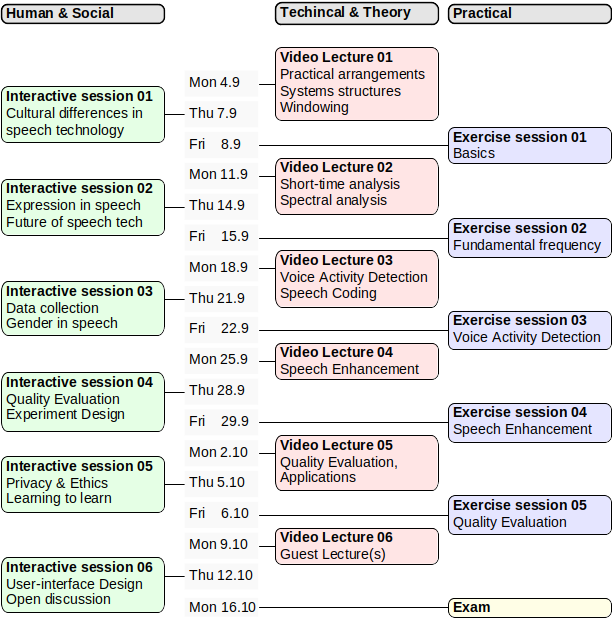
Mon 4.9. Technical & Theoretical
- Practical organization of course
- Why speech processing? video, book
- Linguistic structure of speech. book
- Applications and systems structures. video, book
- Speech production, book
- Waveform, Short-time analysis, Windowing, Signal energy, loudness and decibel, Spectrum, Envelope and Formants, Fundamental frequency, Spectrogram, Autocorrelation, Cepstrum. book, videos
- Mel-cepstrum and the MFCC. book, videos
Thu 7.9. Human & Social
- Applications of speech technology
- Cultural differences in speech and in the use of speech technology, including differences in both regional areas, age groups, and economic/educational background.
Mon 11.9. Technical & Theoretical
- Continuation of videos missed on 4.9.
- Linear prediction and linear predictive coding (LPC), Long-time prediction (LTP), Fundamental frequency, Jitter and shimmer, book, videos
- Short-time processing and the STFT (Accuracy over time = Sampling rate, Accuracy over amplitude = Quantization and pulse code modulation) book, videos
14.9. Human & Social
Expression in speech
We will study how emphasis and the fundamental frequency can be used to change the meaning of utterances. For example, the word "party" can be spoken such that it becomes a question, an exclamation, a neutral statement or a disappointment (try it!). Party? Party! Party. Party...You will be assigned into groups of approximately 3 people.(Duration 20-30 minutes) In your group, device examples of short sentences, where you can change the meaning by only changing speech characteristics such as emphasis, tone, fundamental frequency, whisper/shouting etc. Try to come up with examples of at least- Question vs. statement
- Different emotions (Excited, sad etc.)
- Ironical and joke vs. factual and serious
If you like, you can also try- Different levels on the public vs intimate axis (talking publicly on stage vs. talking to your partner over a romantic dinner)
- Near vs far (to other speakers)
- Speed of speech - can that change meaning?
- Volume of speech (shouting vs whispering) - can that change meaning?
- Rough vs. smooth - can that change meaning?
- High vs. low pitch - can that change meaning?
- Other?
Afterwards, each group can present a selection of their best sentences for the whole class.Future of speech technology
For preparation: Think about sci-fi movies, what speech technology they present and how it is used?Where will speech technology go in 5 years, 10 years, 20 years and 50 years?For inspiration, think about what technology would be needed to achieve these scenes from sci-fi moviesFocus especially on- The acoustic speech signal processing (not so much the natural language processing or the artificial intelligence) and
- What works and what does not work properly. Why does it not work?
Finally, do you think that all interfaces will be spoken in the future? Why do you think so or why not?Mon 18.9. Technical & Theoretical
Thu 21.9. Human & Social
Data collection
When and where is speech data needed? Where does it come from? What is good data and how can we evaluate the quality of data? How can we collect good data?Gender in speech
The classic approach in speech data collection has been to ask for some background information about speakers, like their age and gender. Today, this feels outdated and awkward. We'll start with the "trivia", why does it feel bad? We'll then continue to discuss the purpose of such labels and try to come up with better solutions. This is an ongoing topic of discussion where there is no consensus in the research community.Mon 25.9. Technical & Theoretical
Thu 28.9. Human & Social
Quality Evaluation (book, videos)
What does it mean to be "good" in speech technology? How do collect evidence of quality? How is quality evaluation different during research and development of algorithms and technologies, choosing solutions for complete systems, when buying speech technology as a company or as a user, and when technology is in use as a service provider, company buying a service, or as an individual user?Experiment Design (book)
How do we plan and execute research or development projects within speech technologies?Mon 2.10. Technical & Theoretical
Thu 5.10. Human & Social
NB: A teaching quality evaluation panel will be observing this lecture. Let's not let that disturb us.Privacy & Ethics in Speech Technology
Learning to Learn
At this stage of the course, you have already learned some basics about speech technology and its algorithms. You have also practiced the application of your learnings in the exercises. What concrete things have you learned? How did you learn those? Importantly, how can you learn better?Many specific technologies and algorithms that we study in this course might be outdated by the time you graduate (gasp!). What useful things can we then learn here? Hint: it's in the titleMon 9.10. Technical & Theoretical
- Tiina Lindh-Knuuttila, Lingsoft (slides)
- Thomas Forss, StageZero Technologies
Ask questions from speakers at https://presemo.aalto.fi/elece5500 .Thu 12.10. Human & Social
Open Discussion and Comments
Any questions left after the course? For example, questions or feedback about- the exam
- grading
- course content
- learning material
- course format and teaching methods (lectures, exercises, exam etc.)?
-
Presentation slides from LingSoft File PDF
- Practical organization of course
