25E52000 - Market Entry Strategies for Entrepreneurial Business, Lecture, 11.1.2022-25.2.2022
This course space end date is set to 25.02.2022 Search Courses: 25E52000
Glossary
Browse the glossary using this index
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
P |
|---|
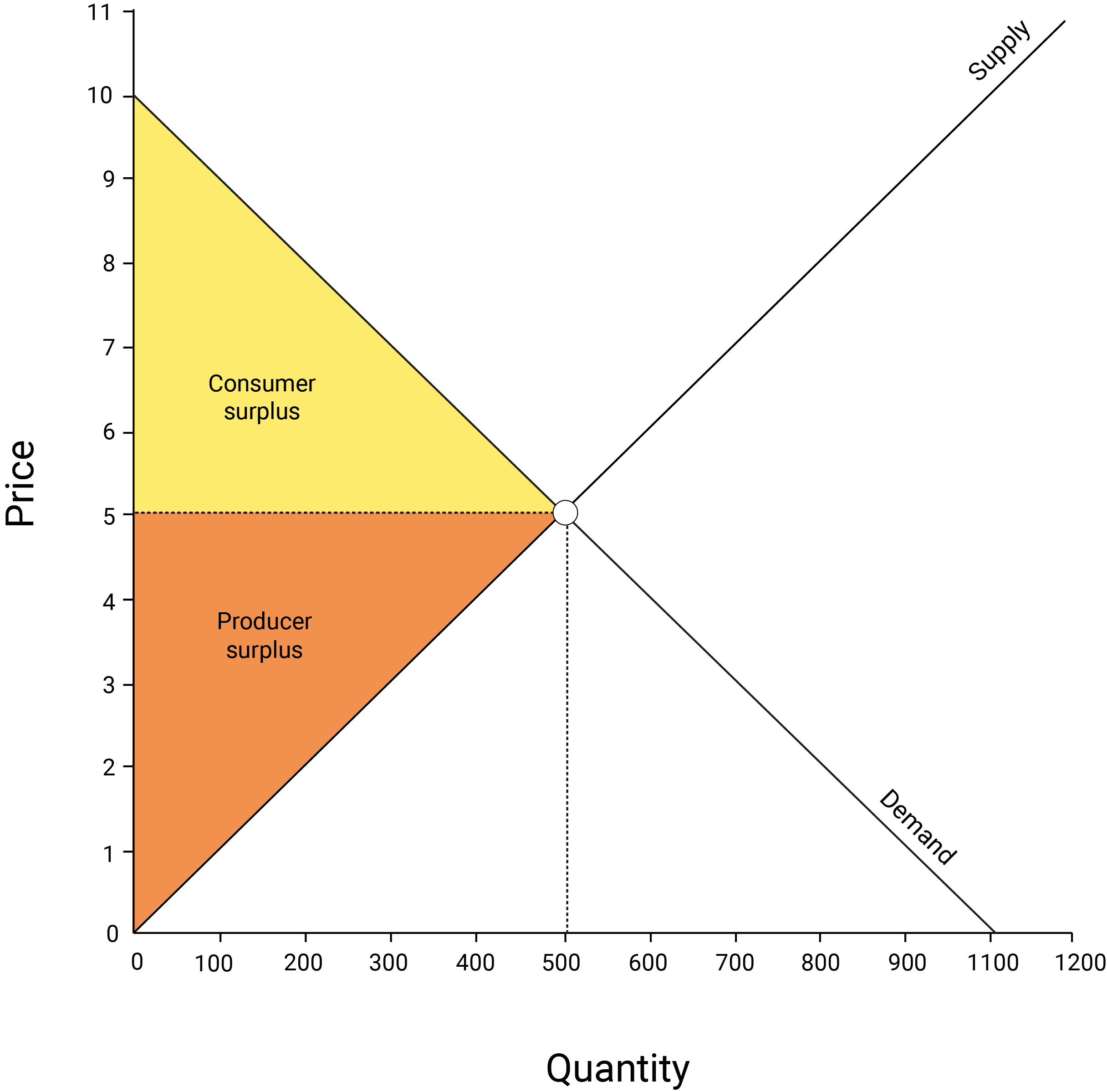
P=MCPrice equals marginal cost, meaning the price just
covers the cost of producing that unit of beer but selling that unit of beer
does not generate any profit. | ||
producer surplusProducer
surplus is the flip side of consumer surplus. It is defined as the difference
between the price (P) that the consumer pays for the product, and the cost (C)
to the firm of making that product. If P – C > 0, the firm is making money
and generating producer surplus.
| ||