MUO-C1071 - Pintasuunnittelu ja värimenetelmät, Luento-opetus, 6.9.2022-2.12.2022
This course space end date is set to 02.12.2022 Search Courses: MUO-C1071
Epson SureColor SC-F2100

Epson SureColor SC-F2100 is a DTG (direct to garment) -printer that uses CMYK inks, plus white for dark and colored bases. Epson Ultrachrome
DG inks are water-based pigment inks with good fastness. The colors work on a wide variety of fabrics such as cotton, 50/50 cotton-polyester blend, silk and viscose. When printing on 100% cotton, the inks meet the Oeko-Tex standard. Epson UltraChrome
DG Ink has been awarded the OEKO-TEX® ECO PASSPORT certification.
Digital textile pigment inks vs traditional pigment dispersions
Pigments are completely or nearly insoluble in water. Pigments are usually from inorganic compound and they do not have affinity to the fiber. Therfore they are applied on to the fabric with binder that fix the inks or dispersions on top of the surface. This makes traditional pigment dispersions suitable almost all fiber type.
Traditional pigment dispersions are usually mixed with printing paste that consist of binder, synthetic thickener and water, in addition some auxiliaries according to need. Digital textile pigment inks on the contrary are liquid form compined with pigment, carrier fluid and binder. This absence of thickener makes tactile feel of digital textile pigment inks more or less almost like reactive dyes.
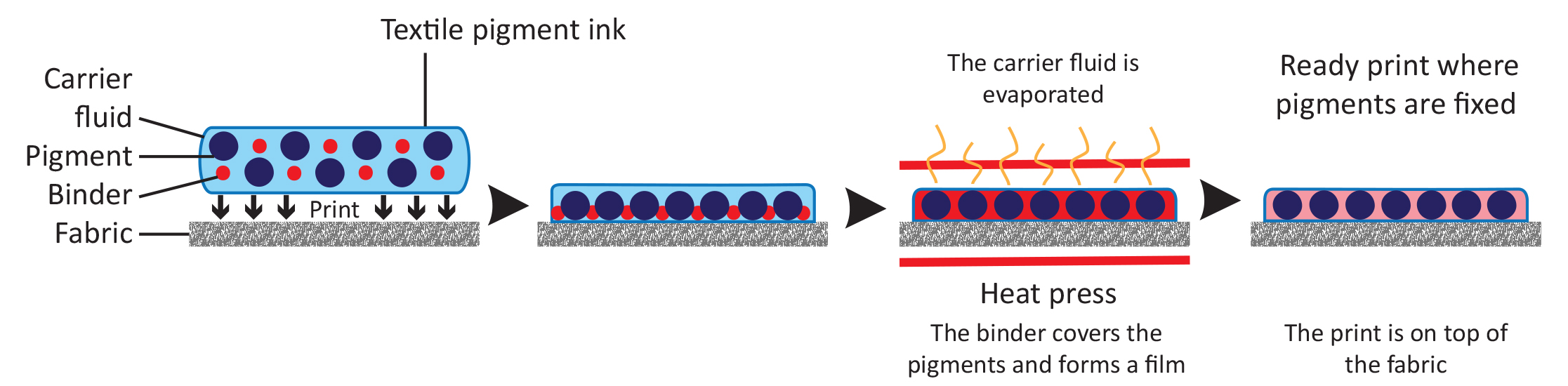
Process of printing with pigment inks is simple (print, dry, cure/fix) and the ink is more or less on top of the fabric or fiber.
Printing to colored or dark bases requires the use of white ink and the handle is more similar to traditional pigment dispersions with thickeners. When printing with white ink, you need to apply pre-treatment liquid. Applying pre-treatment liquid allows the white ink to develop creating a more vivid color.
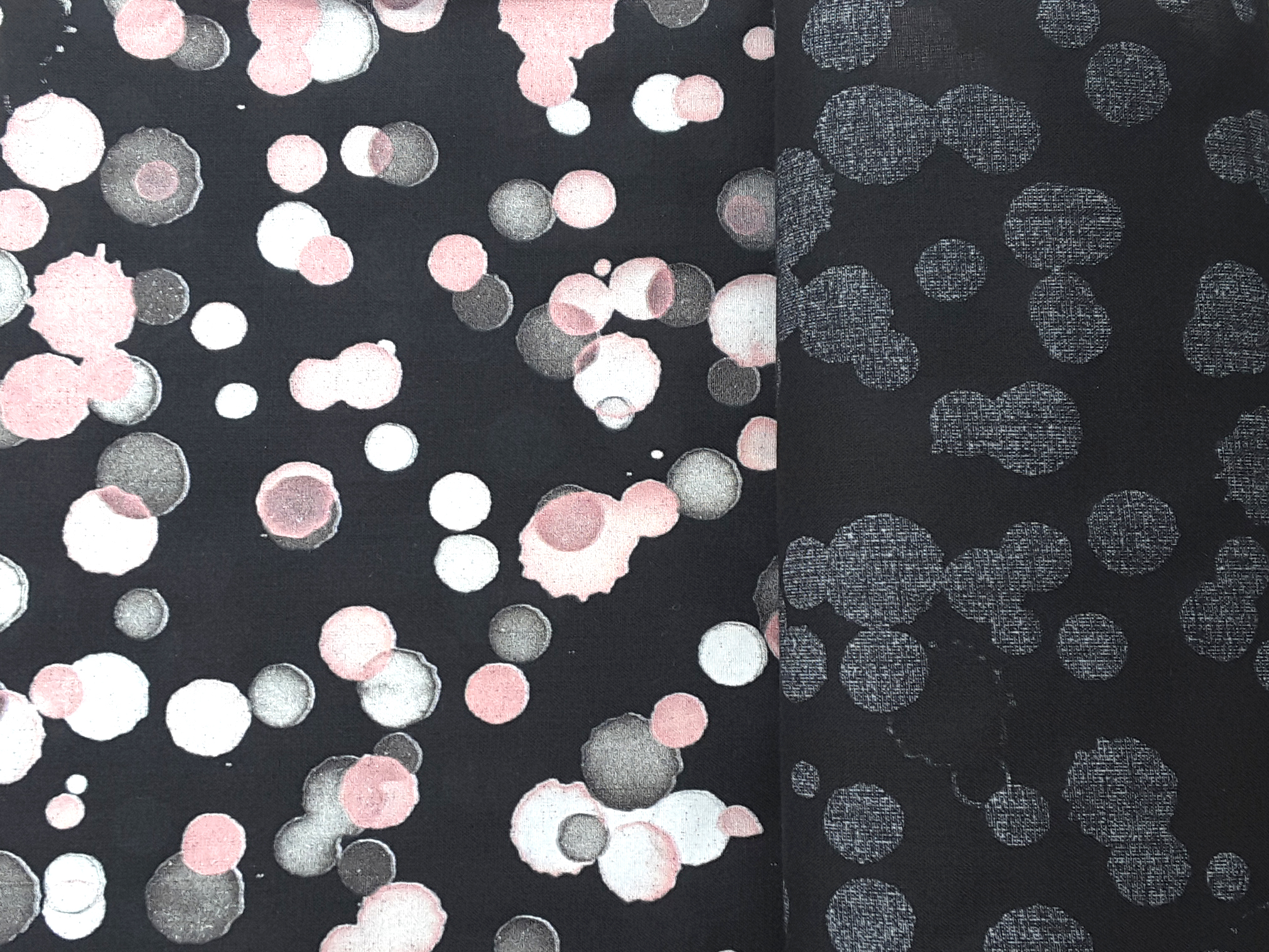

Printing pure colors on colored base requires the use of white ink and pre-treatment. White ink is printed on background first as if it were "white paper" on which the colors are printed.
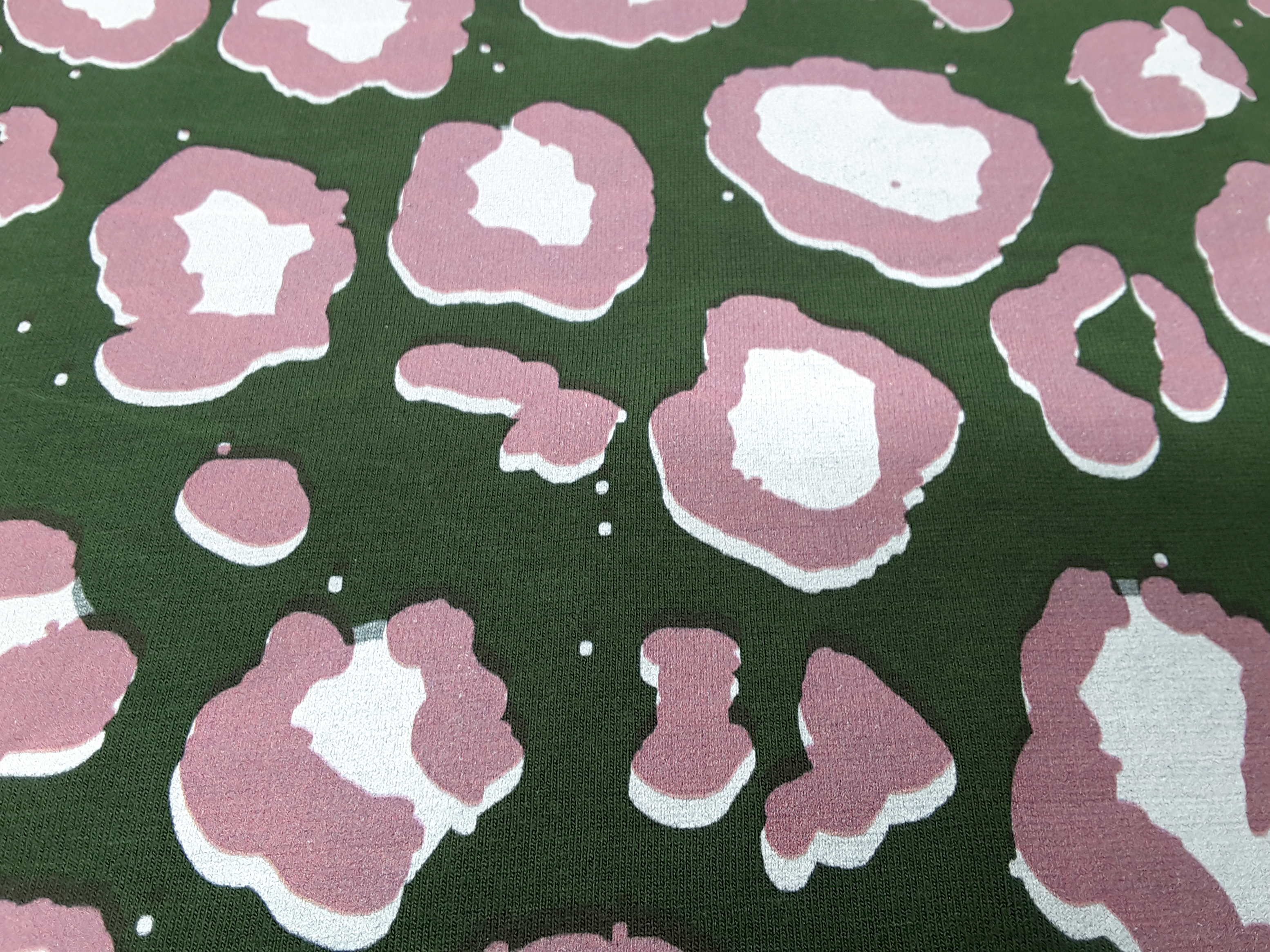
Here the print base (WH Viscose elastane) got so wet that it rose to the humps and the height of the printing platen needed to lower during printing process. Therefore the color print did not match the white bottom.
Possibilities and limitations of pigment printing
Pigment dyes have good lightfastness, but generally poorer wash and abrasion resistance than, for example, reactive or sublimation dyes, which become part of the fiber in the finishing process. The pigment dye adheres to
the fabric or fiber by means of an adhesive (binder), leaving the print more on the surface of the fiber or fabric.
Pigment prints are best suited for purposes where abrasion resistance is not as important as, for example, light fastness.
+
applies to many different fibrous materials (may require primer=pre-treatment)
+ finishing agents usually on the fabric do not bother (hydrophobic surface prevents the absorption of digital pigment ink)
+ simpler process (printing + dry heat
fixing)
+ no wet finishes, dimensional stability
+ light fastness
- abrasion resistance
- washability (can be improved with primer)
- colors in the adhesive layer on the fabric surface (effect on tactile and other properties, especially
on dark bases due to white base color)
